In the realm of health and fitness, the Body Mass Index (BMI) calculator is a widely recognised tool used to assess whether an individual’s weight is appropriate for their height. While it is simple and convenient, understanding the science behind BMI calculators and how they work is crucial for interpreting the results accurately. This article delves into the concept of BMI, how BMI calculator work, and the broader implications for health, including how it relates to different types of health insurance.
What is a BMI calculator?
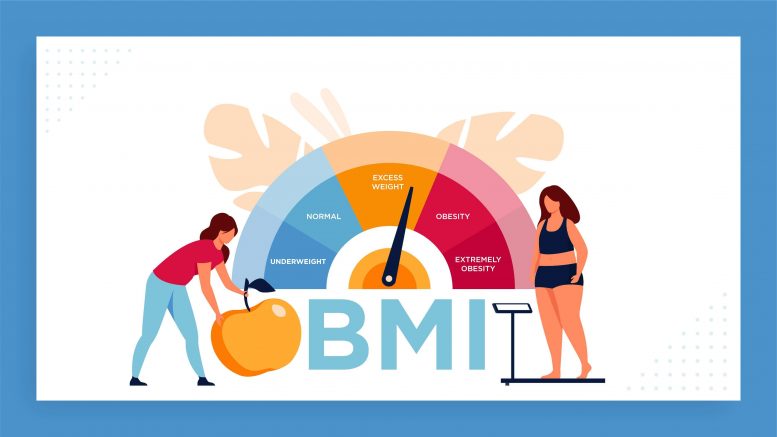
A BMI calculator is an online tool that computes an individual’s Body Mass Index by using their height and weight. The formula used is straightforward: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2. The result places an individual into one of several categories: underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. These categories are based on standard BMI ranges that have been established by health authorities worldwide.
The simplicity of the BMI calculator makes it accessible and easy to use, which is why it has become a popular method for assessing body weight. However, it’s important to note that while BMI can give a general indication of whether a person’s weight is within a healthy range, it does not provide a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s health.
The science behind BMI: What does it measure?
The Body Mass Index was developed in the 19th century by Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet. It was intended as a simple way to measure the relationship between a person’s weight and height. The underlying assumption is that an individual’s weight should be proportional to their height to maintain good health.
BMI is primarily used as an indicator of body fatness, although it does not directly measure body fat. The rationale behind BMI is that as weight increases, so does the amount of body fat. Therefore, individuals with higher BMIs are generally assumed to have more body fat and are at a greater risk of developing weight-related health problems.
However, the BMI calculator has limitations. For example, it does not account for differences in muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution, which means it may not accurately reflect the health of certain individuals. Athletes, for instance, may have a high BMI due to increased muscle mass rather than excess body fat.
Interpreting BMI results: What do they mean?
The BMI scale is divided into several categories that provide a general understanding of where an individual stands in terms of weight:
- Underweight (BMI less than 18.5): Indicates that an individual may be undernourished or have insufficient body fat, which could lead to health issues such as weakened immunity and osteoporosis.
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9): Suggests that an individual’s weight is within a healthy range for their height, reducing the risk of weight-related health problems.
- Overweight (BMI 25 to 29.9): Indicates a higher-than-normal body weight, which may increase the risk of health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- Obese (BMI 30 and above): Reflects a significant excess of body fat, which is associated with a higher risk of serious health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
While these categories provide a useful guideline, they should not be the sole measure of health. Factors such as age, gender, muscle mass, and overall body composition play a critical role in determining an individual’s health status. Therefore, it is essential to use BMI results in conjunction with other health assessments.
BMI and types of health insurance: What’s the connection?
In India, and indeed globally, BMI can influence the types of health insurance available to an individual. Health insurance companies often consider BMI when determining premiums, eligibility, and coverage. Individuals with higher BMIs, particularly those in the overweight or obese categories, may face higher premiums due to the increased risk of health issues associated with excess weight.
However, it is important to recognise that while BMI is a factor in determining health insurance costs, it is not the only one. Different types of health insurance policies may use a range of criteria, including pre-existing conditions, lifestyle habits, and family medical history, to assess risk. For example, a person with a high BMI but no other risk factors may be assessed differently from someone with a lower BMI but a history of chronic illnesses.
Understanding the connection between BMI and health insurance is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage. By maintaining a healthy BMI, individuals can potentially lower their health insurance costs and gain access to a wider range of policies. Additionally, those who are in the overweight or obese categories can explore types of health insurance that offer wellness programs and preventive care, which can help them manage their weight and improve their overall health.
Limitations of BMI: Beyond the numbers
While the BMI calculator is a useful tool, it has several limitations that should be considered. As mentioned earlier, BMI does not distinguish between muscle and fat. This means that individuals with a high muscle mass, such as athletes, may have a high BMI but low body fat, leading to misclassification as overweight or obese.
Additionally, BMI does not account for the distribution of fat in the body. For instance, visceral fat (fat around the organs) is more harmful than subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin), but BMI does not differentiate between the two. Waist-to-hip ratio or waist-to-height ratio are additional measures that can provide a more accurate assessment of health risks related to fat distribution.
Conclusion
The BMI calculator is a valuable tool for assessing body weight relative to height, providing a quick and easy way to determine whether an individual’s weight falls within a healthy range. However, understanding the science behind BMI and its limitations is essential for interpreting the results accurately.
When used in conjunction with other health assessments, the BMI calculator can offer valuable insights into an individual’s health and potential risk factors. Moreover, recognising the relationship between BMI and types of health insurance can help individuals make informed decisions about their health coverage, ensuring they have the protection they need.
In conclusion, while BMI is a useful starting point for assessing health, it should not be the sole measure. A comprehensive approach to health includes considering factors beyond BMI, such as muscle mass, fat distribution, and overall body composition, to ensure a complete understanding of one’s health.