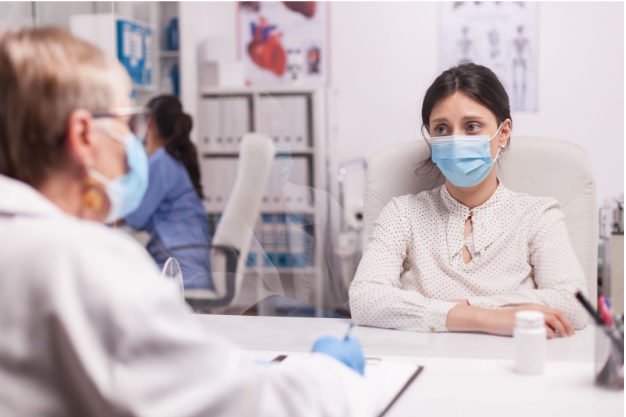
An acute infarct, commonly referred to as a heart attack or stroke, is a critical medical emergency that demands immediate attention. It occurs when blood flow to a part of the body, such as the heart or brain, is blocked, leading to tissue damage. Acute infarct treatment depends on the type (e.g., ischemic or hemorrhagic) and the severity of the infarct.
In this post, we’ll discuss the treatment options for acute infarcts, focusing on medications, stents, and surgery.
What is an Acute Infarct?
An acute infarct or acute stroke is a sudden blockage of blood supply to the brain that leads to cell death. A blood clot or atherosclerosis causes the blockage, where plaque buildup in arteries obstructs blood flow. In the case of a heart attack, this blockage occurs in the coronary arteries, while a stroke affects the blood supply to the brain. Timely administration of treatment can save lives and minimise damage to affected organs.
Acute Infarct Treatment Options
Some treatment options that help manage the stroke situation are;
- Medications for Acute Infarct Treatment
Medications help manage acute infarcts, as they can quickly dissolve blood clots or prevent their formation, restoring blood flow.
Anti-Clotting Medications: Administering anti-clotting drugs helps dissolve the clot causing the infarct. Tissue plasminogen activators (tPA) are commonly used in ischemic strokes and heart attacks to break down the clot and restore blood flow. These medications are most effective when given within a few hours of the onset of symptoms.
Antiplatelet Drugs: Many drugs help prevent platelets in the blood from clumping together and forming new clots. Antiplatelet drugs are essential in managing coronary artery disease, where a blood clot can trigger an acute infarct.
Statins: Statins lower cholesterol levels in patients with atherosclerosis, reducing the risk of plaque rupture and the subsequent formation of clots. These drugs also have anti-inflammatory properties that help stabilise plaque and prevent future infarcts.
Blood Pressure-Lowering Drugs: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart attacks and strokes. Medications that help lower blood pressure, such as ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers, are often prescribed to prevent additional strain on the heart and reduce the likelihood of further infarcts.
Hemorrhage-Specific Medications: For patients experiencing hemorrhagic strokes (due to bleeding in the brain), medications may be used to promote clotting and prevent excessive bleeding. These could include clotting agents or medications that help control blood pressure to reduce the risk of rupture.
- Stents for Acute Infarct Treatment
In certain cases of ischemic heart disease, the use of stents becomes essential. Stents are small mesh tubes that are inserted into weakened or narrowed arteries to provide structural support and improve blood flow.
Placement of Stents in Arteries: In coronary artery disease, where the heart’s blood vessels become blocked, a stent is often placed to help open up the artery and ensure continuous blood flow to the heart muscle. This procedure is commonly performed during a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty.
Prevention of Further Blockage: Stents help to prevent the arteries from narrowing further, reducing the likelihood of another infarct. They act as a physical support to the artery, ensuring it remains open, which can reduce symptoms like chest pain (angina) and improve the overall heart function.
- Surgery for Acute Infarct Treatment
Surgery is usually considered a last resort when medications and stents are ineffective or not appropriate. Surgical intervention for acute infarcts may involve either opening the blocked artery or correcting the damage caused by bleeding in the brain.
Clot Removal Surgery: In the case of a heart attack or ischemic stroke, where the artery gets clotted, surgery may be necessary. This can be done by directly opening the artery or through a catheter-based procedure. Catheter-directed interventions involve using a tube inserted into the blood vessel to remove the clot and restore blood flow to the affected organ.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Surgery: For patients with hemorrhagic strokes, where bleeding occurs inside the brain, surgery may become imperative to stop the bleeding. This could involve clamping the aneurysm or other procedures to seal off the damaged vessels and prevent further bleeding.
Aneurysm Clamping and Repair: In the case of aneurysms (bulging blood vessels) that cause bleeding in the brain, surgical clamping closes off the aneurysm and prevents additional bleeding. This can be a lifesaving intervention, as untreated aneurysms can continue to rupture and lead to severe brain damage.
- Recovery and Follow-Up Care
Following acute infarct treatment, recovery depends on several factors, including the severity of the infarct, the area affected, and the patient’s overall health. Recovery may involve:
Physical Rehabilitation: Patients undergo physical rehabilitation (such as physiotherapy or speech therapy) to regain strength, motor skills, or speech if the infarct affects mobility or cognitive function.
Lifestyle Modifications: After an infarct, patients must make lifestyle changes such as improving their diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress. These changes help lower the risk of future infarcts and improve overall health.
Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are critical to monitor the patient’s recovery, manage ongoing symptoms, and adjust treatment as necessary.
Conclusion
Acute infarct treatment has come a long way, with medications, stents, and surgical procedures offering effective options for managing this condition. Timely treatment can save lives and minimise the damage to organs, whether the infarct occurs in the heart or brain. If you or someone you know is at risk for an acute infarct, seek immediate medical care from Nanavati Max Super Speciality Hospital and discuss the best treatment options. Early intervention and proper treatment are critical to a successful recovery.